Are UVA and UVB Emissions the Same as Sunlight?
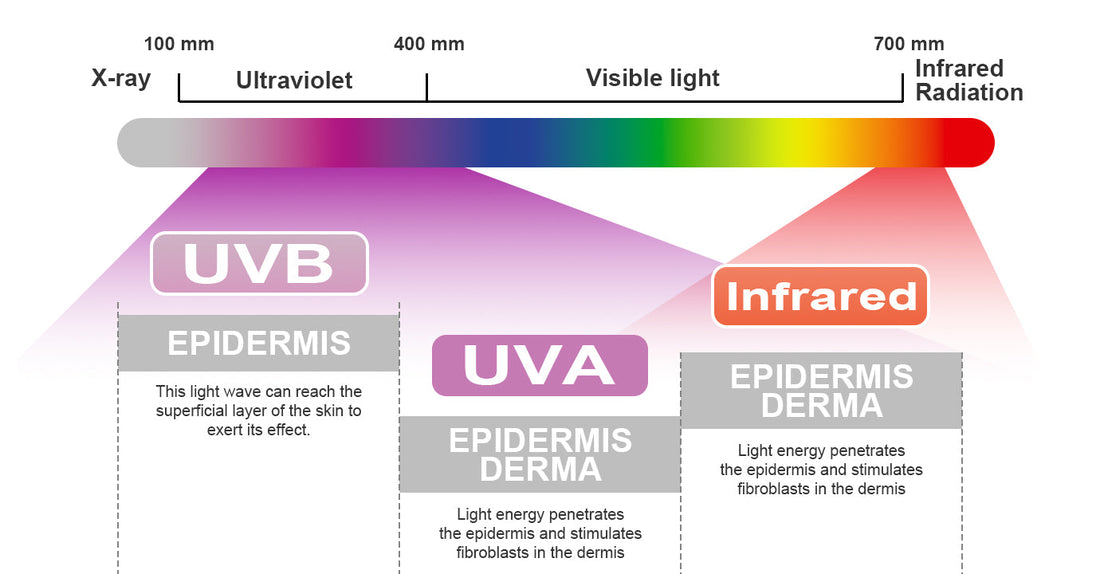
The light emitted by UVA and UVB is essentially the same as the ultraviolet (UV) rays in sunlight, both belonging to electromagnetic radiation. However, there are significant differences in their wavelength distribution, intensity, and biological effects. Here is a detailed analysis:
1. Differences in Wavelength Ranges and Sources
|
Type |
Wavelength Range |
Status in Sunlight |
Typical Uses of Artificial Devices |
|
UVA (Long-wave) |
315~400 nm |
Accounts for 95% of UV rays reaching the Earth's surface; penetrates the ozone layer and reaches the ground directly |
Tanning beds (for bronzing), aging test lamps |
|
UVB (Medium-wave) |
280~315 nm |
Approximately 5% reaches the ground, with most absorbed by the ozone layer |
Medical treatments (e.g., for psoriasis), local sterilization |
|
UVC (Short-wave) |
100~280 nm |
Almost completely blocked by the ozone layer and does not reach the ground |
UV disinfection lamps (main force for sterilization) |
Key Distinctions:
· Sunlight contains full-spectrum UV rays (UVA/UVB/UVC), but only UVA and a small amount of UVB reach the Earth's surface.
· Artificial devices (such as disinfection lamps and tanning beds) emit specific wavelengths selectively:
· Disinfection lamps mainly emit UVC (simulating solar UV rays that do not reach the Earth's surface).
· Tanning beds focus on UVA/UVB, used to simulate tanning or for therapeutic purposes.
2. Comparison of Biological Effects
UVA (Long-wave):
· Strong Penetration: Reaches the dermis directly, damaging collagen and causing skin aging and wrinkles.
· Immediate Damage: Stimulates melanin production, leading to skin darkening and pigmentation.
· Long-term Risks: Damages DNA and increases the risk of skin cancer.
UVB (Medium-wave):
· Acts on the Epidermis: Causes sunburn, redness, and blisters (in the short term).
· Key Function: Promotes vitamin D synthesis, but excessive exposure also damages DNA.
Note: Tanning beds intentionally enhance UVA/UVB output to achieve tanning effects. Their radiation intensity may be higher than that of natural sunlight, requiring strict protection.
3. Necessity of Protection
· UVA Protection: Choose sunscreen products labeled PA+/PA++/PA+++ (or with PPD values). Since UVA can penetrate glass and clouds, protection is needed both indoors and outdoors.
· UVB Protection: Relies on sunscreens with SPF values to prevent sunburn, but they cannot block UVA.
· Risks from Artificial Devices: UVC from disinfection lamps and intensified UV rays from tanning beds require professional protection (such as goggles and time-limited exposure).
Summary
UVA and UVB from artificial sources are essentially the same as those in sunlight. However, sunlight, after being filtered by the atmosphere, is dominated by UVA with a small amount of UVB. Artificial devices can specifically enhance certain wavelengths, resulting in more concentrated biological effects and higher potential risks. Whether it is natural or artificial UV rays, layered protection should be adopted according to their wavelength characteristics.
